Annual Forage (AF), an area-based insurance plan, allows livestock and hay producers to purchase coverage designed to protect against risk associated with lack of precipitation on acreage planted annually to forage, graze or use as hay for livestock.
The Annual Forage program has proven to be an effective risk management tool for a growing number of producers, ensuring the financial stability of their operations during recent years of unpredictable and adverse weather conditions. Your FBN Insurance agent can work with you one-on-one to tailor an Annual Forage policy to meet the specific needs of your operation.

With a Farmers First® mindset at the forefront of every relationship they develop with customers, our FBN Insurance agents consistently aim not just to help you secure AF coverage, but to also develop a holistic risk management strategy customized to your farm and risk tolerance.
Many FBN Insurance agents are livestock producers, too. With years of hands-on ag experience, they’re familiar with the challenges associated with livestock operations and understand the distinct challenges you and your operation may be facing. With their deep insurance expertise and ag knowledge, our agents are ready to help design a customized risk management strategy that works for your unique needs.

What Is Annual Forage?
The Annual Forage program is designed to insure against a decline in an index value that is based on the long-term historical average precipitation for the same area for the same period.
Producers must plant acres annually in order to be eligible for AF coverage. However, they do not need to insure 100% of the planted acres of an annual forage crop to be eligible for coverage. AF coverage is available at six different coverage levels, and the insured party is the user of the acreage, either by land ownership or by lease.
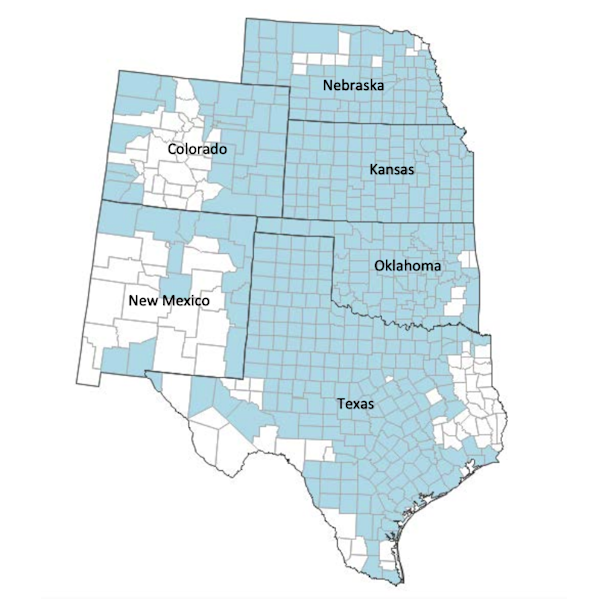
Producers must sign up by July 15 to be eligible for this type of coverage, which is currently offered in:
Colorado | Nebraska | Oklahoma | South Dakota |
Kansas | New Mexico | North Dakota | Texas |
It is important to note that AF is not drought insurance and does not insure against abnormally high temperatures or windy conditions.
How Does Annual Forage Insurance Work?
Annual Forage coverage is divided across 12 growing seasons, also known as insurance periods, which are determined by the dates the acres were planted. Producers can divide their liability into two-month index intervals targeting the timeframe in which precipitation is most important for the crop being planted.
Not all growing seasons are available across all states. For example:
December and January are not available in Colorado, Kansas, and Nebraska.
December, January and February are not available in North Dakota and South Dakota.
Similar to the 12 available growing seasons, there are also 12 acreage reporting dates. Acreage Reporting dates are based on planting months; producer acreage reports are due the 5th of the month following the planting month. Acreage reports must be submitted by the due date to have coverage for the particular growing season.
For more information about growing season eligibility, acreage reporting dates and other coverage details, contact an FBN Insurance agent.

What Is the Dual Use Option for Annual Forage?
Annual Forage coverage also offers a Dual Use Option. This allows a small grain producer to insure under Annual Forage for grazing in the winter/early spring and then insure their grain crop with a separate MPCI policy while remaining eligible to maintain both benefits.
The Dual Use Option is available in counties where grain/grazing is considered a good farming practice, which includes select counties in:
Colorado | New Mexico |
Kansas | Oklahoma |
Nebraska | Texas |
Dual use option is only available for Growing Seasons 1, 2, 3 and 4, which includes index intervals. The option is primarily utilized to cover wheat, but some counties also include barley and oat coverage. Your FBN Insurance agent can check the Annual Forage and small grains special provisions of insurance for more details.
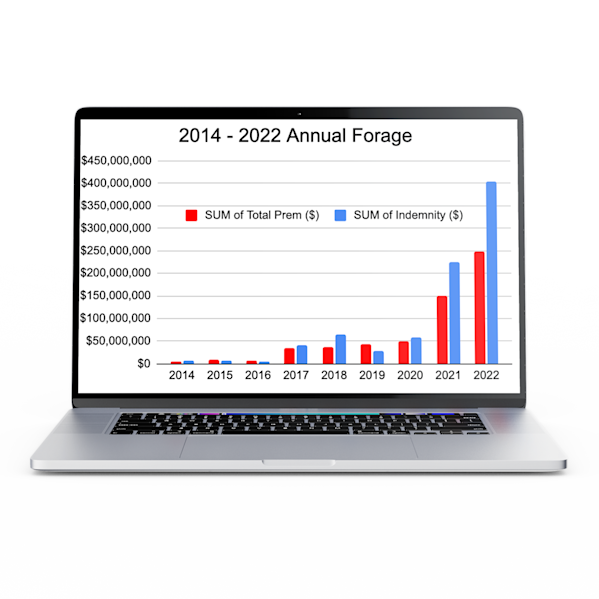
Annual Forage Indemnity Payments
After the producer’s selected two-month interval ends, the United States Department of Agriculture’s (USDA) Risk Management Agency will release a Final Grid Index value representing how much precipitation was recorded for the Grid to compare against the producer’s coverage level.
Each grid covers an area equal to .25° latitude x .25° longitude. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) creates these grids, which do not follow state, county or national boundaries. Each grid is individually rated based on the data for that grid. (For example, in the middle of the country the area in a grid equates to about 150,000 acres or a 15x15 mile square. In North Dakota, the grid narrows to about 130,000 acres and in South Texas stretches up to about 196,000 acres.)
There is no loss adjustment. If there is a loss, the indemnity is automatically calculated and then paid.
Connect With An Agent
Connect With An Agent
Complete the form below to speak with an FBN representative about Annual Forage coverage today, or call (866) 878-7133.
Strategically Manage Risk with FBN
Supported by a Farmers First® approach to everything we do, FBN Insurance offers a variety of coverage options to support you as you maintain and scale your ag operation. In addition to livestock risk protection, FBN Insurance also offers:

PRF

Apiculture

MPCI

Crop-Hail

WFRP

Health

And More
FAQs
What is the Rainfall Index and how does it work?
The Rainfall Index (RI) is based on weather data collected and maintained by NOAA’s Climate Prediction Center, which is a data set used in the Annual Forage Program. The index reflects how much precipitation is received relative to the long-term average for a specified area and timeframe.
Producers must choose at least two, 2-month periods when precipitation is important for forage growth to their operation. These periods are called index intervals. RMA uses NOAA CPC data to calculate normal precipitation and deviations from normal precipitation. RMA uses NOAA precipitation data based on the Optimal Interpolation methodology. Interpolation is based on the idea that things closer together in space are generally more similar than those farther apart and it estimates precipitation for a grid using reporting stations within a search radius around the grid.
What does “area-based” mean?
“Area-based” means coverage is not based on an individual producer’s experience but coverage is based on a grid’s deviation from normal experience. For example, if a ranch receives a surplus of rain but the grid area was below average, you could receive a payment or vice versa.
What is a grid?
A grid is the physical area under which your operation is insured. You are paid based on the losses interpolated to the grid for the Rainfall Index, which is why it is important that you choose the right grid(s) in which your operation is located.
How do I know which grid to choose based on the location of my acreage?
FBN agents have access to innovative mapping systems to assist you in determining which grid(s) your acreage falls within to make sure you purchase the appropriate coverage.
How do I know which index intervals to choose?
The index intervals you insure and how much you insure for each interval is important. It is important to review the historical indices tools for your grid along with past production records to determine if these programs work for your operation. It is also important to assess which index intervals correlate well to your production.
FBN agents are available to provide guidance tailored to your unique insurance needs and assist you with making informed decisions for your farm’s success. In addition, FBN members have access to a custom decision support tool that helps them make an informed decision on which index interval is best suited to their operation.
Do I have to insure all of my planted acres?
No. You may elect to insure less than 100% of the planted acres.
How are losses triggered?
When the interpolated precipitation for the grid falls below average for the index interval, it triggers a loss payment. Producers do not need to submit a loss claim or notify their agents. RMA calculates any loss and your insurance company processes any indemnity due. Losses are calculated based on whether the current year’s precipitation in a grid has deviated from normal compared to the historical normal precipitation in the same grid, for the same period. Losses are not based on a single ranch or a specific weather station in a general area.
The Latest Livestock Risk Management Insights

How Annual Forage Insurance Can Stop You From Worrying About Drought

When Are Livestock Insurance Deadlines?

Do You Need Annual Forage, PRF or LRP Insurance Coverage?

Webinar: Annual Forage: How To Protect Against Drought
